Chemistry
Isotopes - Definition
Isotopes are variations of chemical elements. All isotopes of an element have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons (Friedland and Relyea, 2015).
Isotopes in Fission
In nuclear fission, a radioactive isotope must be split to produce heat. The isotope that is used in a nuclear power plant to begin nuclear fission is Uranium-235. It is an isotope that undergoes fission with relative ease. Uranium has a molecular mass of 238.03 grams per mole and U-235 has 92 protons and 143 neutrons (Friedland and Relyea, 2015). It can be found in uranium ores, which are areas of uranium found in the Earth's crust (Uranium Recovery, 2015).


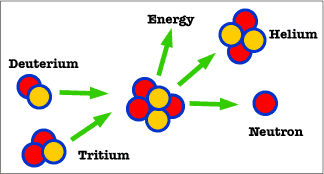
Isotopes in Fusion
In nuclear fusion, the light nuclei of two hydrogen atoms are typically used to begin the reaction. Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, which means that it usually contains one proton and one neutron. Hydrogen-2 (deuterium) and hydrogen-3 (tritium) are the isotopes of hydrogen used in fusion. H-2 has one proton and one neutron, the standard for hydrogen. H-3 has one proton and neutrons. When these hydrogen isotopes are fused they create the nuclei of helium, a heavier atom. This helium isotope is helium-4, which contains two protons and two neutrons (Friedland and Relyea, 2015).